A radon gas monitor is an essential device designed to detect radon gas concentration within indoor spaces and provide ongoing assessment of radon levels. We recommend every home have a continuous radon monitor for your and your family’s safety.
These monitors range from simple passive kits to sophisticated digital instruments that offer more extensive data and advanced features like environmental measuring and data logging.
Ensuring that your real-time radon monitor is effectively installed and properly maintained is crucial for accurate readings. At the same time, technological advancements have made radon monitoring more user-friendly and accessible to the average homeowner.

Understanding Radon
Having witnessed the impact of this silent and lethal threat, I can attest to the consequences as a Certified Consultant specializing in Radon and Indoor Air Quality.
Radon is a naturally occurring radioactive gas you cannot see, taste, or smell. It’s derived from the natural breakdown of uranium in soil, rock, and water. Here’s what you need to know.
Radon Basics
Radon is a byproduct of the radioactive decay of uranium, an element found in varying amounts in the soil and rock beneath your home, in well water, and in some building materials.
Radon gas diffuses from the ground into the outdoor air but can become a health concern if it accumulates indoors. Since radon comes from the radioactive decay of uranium, it constantly produces alpha particles, a form of ionizing radiation.
The Importance of Radon Monitoring
Your home is your sanctuary, but radon gas can turn it into a health hazard. Radon is the second leading cause of lung cancer, making it a silent but deadly presence in homes across the country.
The only way to know if your home is affected is through vigilant long term radon monitoring. I recommend all households have a high-quality radon detector, like the Airthings Corentium or the Ecosense RadonEye, which offers peace of mind, ensuring your living space remains a safe haven for you and your loved ones.
While continuous radon monitoring is important, it should not replace a permanent radon mitigation system to reduce high radon levels in your home.
Health Implications of Radon Gas Exposure
Exposure to radon gas is a concern because it’s a radioactive gas that can damage lung tissue and lead to lung cancer. You are most at risk from radon exposure in your home, where you spend most of your time.
Long-term radon exposure can be harmful to your health, with radon being the second leading cause of lung cancer after smoking.
Radon in the Environment
Radon levels in the environment can vary widely, primarily due to the geology beneath your home and environmental factors. Methods such as utilizing a radon-thoron discriminative monitor can aid in assessing environmental radon levels effectively.
Invariably, it’s essential to test the indoor air in your home to determine your family’s risk level, as radon is unsafe at any concentration, and recommended action levels have been set to manage the risk.
Radon Gas Monitoring Technology
Radon gas monitoring is essential to ensure indoor environment safety, as radon gas is a well-known health hazard. Today’s technology allows you to continuously track radon levels with high accuracy using advanced monitors with user-friendly interfaces.
Choosing the Right Radon Detector
Precision, reliability, and ease of use are paramount when selecting a radon detector. Consider these factors:
- Type of Detector: Choose between digital radon detectors for instant readings or long-term radon test kits for a comprehensive assessment.
- Smart Features: Opt for a smart radon detector with Wi-Fi connectivity, like the Airthings View Plus, to remotely monitor your home’s radon levels.
- Battery Life: Ensure your radon gas monitor is battery-operated for uninterrupted monitoring, even during power outages.
- Additional Sensors: Some real time radon monitors, such as the Airthings Corentium Pro, come equipped with humidity and temperature sensors, offering a holistic view of your home’s air quality.
Types of Radon Detectors
Radon detectors come in various forms, each designed for specific monitoring needs. Passive detectors, such as charcoal canisters and alpha track detectors, do not require power and are ideal for short-term testing.
These are often sent to a laboratory for analysis after the testing period. Active detectors operate using electricity or batteries and can provide continuous monitoring.
They usually feature a display for easy reading; some even incorporate a touchscreen interface for enhanced interaction.
Features of Modern Radon Monitors
Modern radon monitors distinguish themselves with a suite of advanced features. A critical aspect of these devices is their accuracy, maintained through regular calibration. Contemporary models often include:
- Continuous Radon Monitoring: With memories that can pinpoint radon levels over time, these monitors allow for ongoing assessment of the radon concentration in your space.
- Connectivity Options: Many devices connect via Bluetooth or USB to sync data with an app or OneRadon software, giving you easy access to radon readings.
- User-Friendly Interfaces: Products like those from Airthings provide ease of use with simple, clear displays and sometimes touchscreen capabilities.
- Power Options: Flexibility is offered through the choice of power source, from plug-in models to those with long-life batteries.
Regular use of radon detectors can be vital in maintaining a healthy indoor environment. With evolving technologies, being proactive about monitoring radon levels in your home or business is simpler than ever.
Installation and Maintenance
Radon monitors are sophisticated instruments that require correct setup and regular maintenance to provide accurate readings. Your vigilance in installation, calibration, and ongoing upkeep is vital to their performance.
Installation and Maintenance
Proper placement and maintenance are crucial for accurate radon detection:
- Location: Install your radon monitor in the lowest level of your home, where radon levels are likely to be the highest.
- Maintenance: Regularly check the battery and Wi-Fi connectivity to ensure your radon detector operates flawlessly.
- Calibration: Some digital radon monitors may require periodic calibration. Refer to the manufacturer’s guidelines to maintain accuracy.
Setup Process
Installing your radon monitor begins with choosing an appropriate location, away from doors, windows, and other areas susceptible to external airflow. Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines carefully to ensure optimal placement.
For example, a study on radon mitigation systems suggests installing continuous radon monitoring (CRM) instruments to track levels over time. You must respect installation procedures to maximize the device’s effectiveness and accurately assess radon levels.
Calibration and Accuracy
Calibration configures the radon monitor to measure radon levels within a predetermined accuracy range. Depending on the model, your monitor may require professional calibration periodically—often annually—to maintain accuracy.
Refer to your device’s manual to understand the interval and duration of calibration. Accuracy is critical in the work involving a radon detector and ionization chamber to ensure quality readings in specific environments.
Maintenance and Battery Life
Regular maintenance, including checks and unit cleaning, is paramount to sustain the monitor’s longevity and reliability. For most models, plan on a semi-annual maintenance schedule.
Attention should be given to the device’s battery life, which can vary widely but typically needs replacement or recharging every 6 to 12 months.
It is important to note signage of any technical failures or need for repairs during routine maintenance, as advised by networks such as the Italian Radon Monitoring Network (IRON), which emphasizes continuous functioning without breaks due to technical issues.
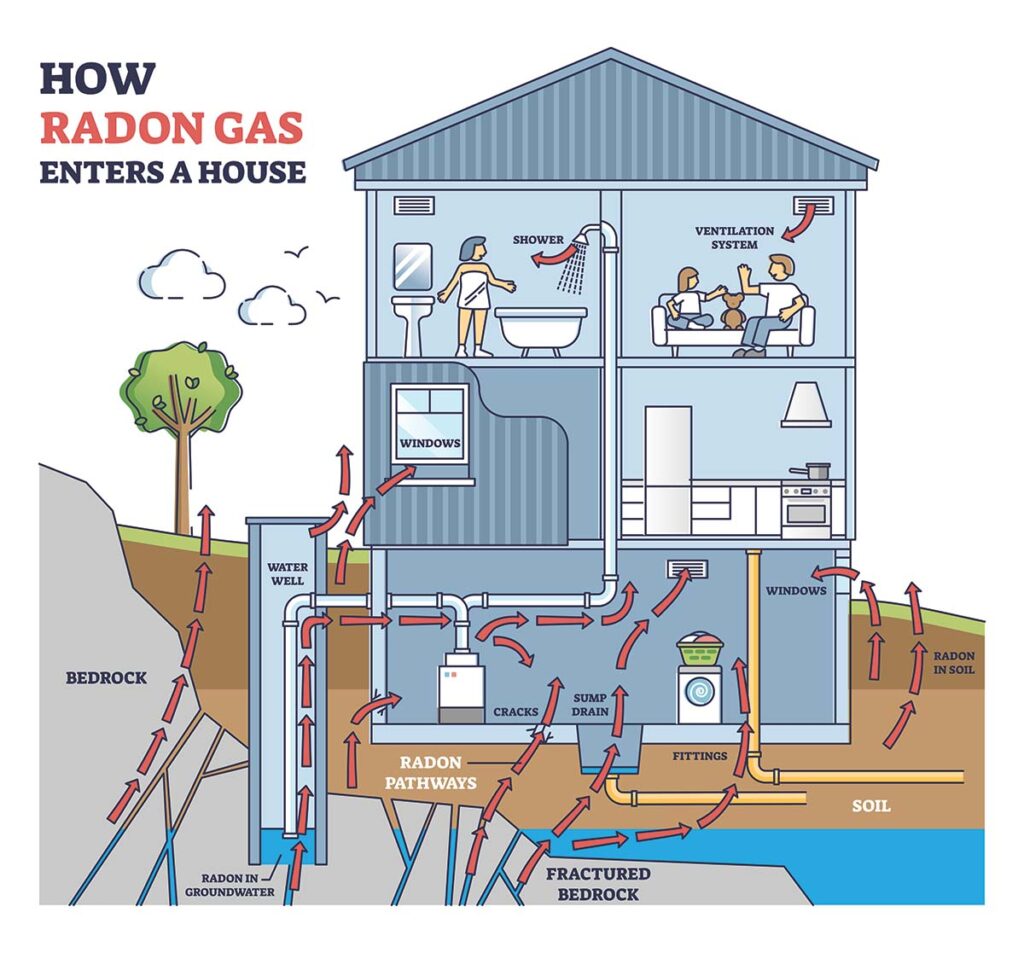
Radon Detection and Mitigation
Radon detection and mitigation are essential to ensure your home’s indoor air quality is safe. Accurate radon level readings can guide effective strategies to reduce long-term exposure risks.
Reading Radon Levels
You’ll likely opt for a continuous radon gas monitor, which offers real-time tracking and greater accuracy when monitoring radon levels.
These devices, certified by organizations like the NRPP (National Radon Proficiency Program), C-NRPP (Canadian-National Radon Proficiency Program), or NRSB (National Radon Safety Board), provide detailed insights into the fluctuations of radon in your indoor environment.
To start, place the monitor in the lowest lived-in level of your home and follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for the initial reading duration.
Interpreting the Data
Understanding the readings from your radon detector is essential for taking appropriate action:
- Safe Levels: The EPA recommends action if radon levels exceed 4 pCi/L. However, no level of radon exposure is considered completely safe.
- Immediate Action: If your long term radon detector indicates high levels, confirm the results with a short-term radon test kit and consult a radon mitigation professional.
Once you’ve collected data on indoor radon levels, interpretation is key. The EPA has set an action level of 4 pCi/L (picocuries per liter), so if your continuous monitor shows readings above this threshold, it indicates a health risk from long-term exposure. Data analysis should also consider seasonal variations, as radon levels can fluctuate.
Mitigation Strategies
If radon mitigation is necessary, soil depressurization is common, which involves adjusting the pressure differential between your home and the soil beneath to redirect radon gas outdoors.
Other strategies might include sealing cracks in foundations or increasing ventilation. Always hire a mitigation professional with NRPP, C-NRPP, or NRSB certification to ensure the work is done safely and effectively. Remember, mitigation is not a one-time fix; you should continue to monitor radon levels post-mitigation to ensure they remain low.
Advanced Monitoring Features
In embracing the latest technology, your radon monitoring features extend beyond simple detection. They facilitate integration with smart systems and enhance the management and sharing of critical data, ensuring you stay informed and proactive in radon safety efforts.
Smart Integration
Your smart radon detectors are more than mere measurement devices; they are now part of a connected home ecosystem. Equipped with features like Wi-Fi connectivity, these advanced units integrate seamlessly with your smart home devices.
For instance, the Airthings Corentium detector syncs with a mobile app, allowing you to monitor radon levels directly from your phone. This direct integration makes receiving real-time notifications and alerts possible, so you can take immediate action if radon levels rise.
- Push Notifications: Receive alerts on your mobile device if radon levels exceed a certain threshold.
- Voice Assistant Compatibility: Use voice commands to inquire about the current radon levels through integrations with assistants like Amazon Alexa or Google Home.
Data Management and Sharing
Embracing digital radon tests allows for effective data management and sharing. Your radon monitor collects data over time, providing a detailed background on radon levels in your environment, which is crucial for assessing long-term trends and uncertainty.
- Long-Term Tracking: Store and review historical radon level data to identify patterns or seasonal changes.
- Data Export: Share your radon data with experts for further analysis or integrate with home automation systems for advanced response strategies.
The integration of mobile apps ensures that you can manage this data conveniently. You can view a digital log and call for professional support through the app. This digital approach offers a comprehensive understanding of radon levels and the practicality of managing them smartly and effectively.

Environmental Measuring
You must utilize precise environmental measuring tools to understand radon levels comprehensively. This includes a thorough air quality assessment coupled with the use of supplementary ecological sensors.
Air Quality Assessment
Measuring radon in your environment necessitates using air quality monitors that specifically detect this invisible gas. Radon concentration can fluctuate based on various conditions, such as airflow, humidity, and even temperatures.
An effective radon monitoring system will give you data about these factors to help you assess the overall indoor air quality.
- Radon: Principal component of air quality concerning lung cancer and other lung disease health risks.
- VOCs (Volatile Organic Compounds) Should be monitored as they can contribute to indoor pollution levels.
- Indoor Air Quality: A comprehensive measurement includes radon, VOCs, and other pollutants.
Supplementary Environmental Sensors
In addition to radon, a robust environmental monitoring approach includes humidity, pressure, and temperature sensors.
- Humidity: High levels can influence radon release and trapping indoors.
- Temperature: Affects how radon moves within your environment and its detection.
- Pressure: Differences between indoors and outdoors can drive radon into buildings.
Integrating these environmental sensor readings gives you a detailed perspective on the conditions that affect radon levels, allowing for more effective mitigation strategies.
Radon Mitigation: Taking Action for a Safer Home
Once your radon detector alerts you to elevated levels of this hazardous gas, acting swiftly and decisively is crucial. Radon mitigation isn’t just about immediate correction; it’s about ensuring long-term safety and maintaining optimal air quality in your home. Here’s how you can tackle the issue head-on:
Professional Radon Mitigation Services
- Seek Expertise: Contact a certified radon mitigation specialist who can assess your situation and recommend the best action.
- Mitigation Techniques: Common methods include sub-slab depressurization, where a vent pipe and fan system draw radon from beneath your home and release it outside.
- Post-Mitigation Testing: After the mitigation system is installed, use your radon detector, like the Airthings Corentium Home, to continuously monitor radon levels and ensure the effectiveness of the mitigation efforts.
DIY Radon Reduction Methods
While professional mitigation is recommended, there are steps you can take to reduce radon levels:
- Seal Cracks: Use caulk to seal cracks in your home’s foundation and walls, reducing the entry points for radon.
- Improve Ventilation: Increase airflow in your basement or crawl space to dilute radon concentrations. Simple measures like opening windows or installing additional vents can make a difference.
- Test Regularly: Even after mitigation, regular testing with a reliable radon test kit is crucial to ensure that radon levels remain low.
When selecting a radon monitor, it’s essential to factor in certain elements beyond basic radon level measurements. Your home’s unique traits and additional device health and safety features are pivotal.
Home Construction Factors
Your home’s construction significantly impacts indoor radon levels. If your residence has a basement or is built on a slab-on-grade foundation, inspecting for cracks is crucial, as radon gas easily infiltrates these openings from the soil beneath.
Radon levels can also be high in homes with crawl spaces, necessitating proper ventilation or barrier installation. When choosing a radon monitor, one that can account for these variations ensures more accurate readings.
Health and Safety Extras
Certain models may include a tamper sensor to ensure the integrity of your readings. USB-C connectivity allows for easy data transfer and device updates. Some monitors also detect other environmental variables like mold, dust, pollen, and carbon dioxide.
If you prefer a system that can connect remotely, look for a monitor with LTE cellular modules for constant updates, especially if you’re often away from home. This integration adds an extra layer of security to your radon monitoring system.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the best radon monitors available on the market?
When looking for the best radon monitors, consider a continuous radon monitor like AirThings offering comprehensive results over extended periods. These are reliable digital radon monitors that provide ongoing readings.
How can I ensure the accuracy of my home radon tester?
To ensure the accuracy of your home radon tester, follow the manufacturer’s instructions carefully, which may involve placing the device away from drafts, high humidity, and other environmental factors that could skew the results.
What are the average costs associated with purchasing a radon monitor?
The cost of purchasing a radon monitor varies, from $15 for basic short-term test kits to several hundred dollars for advanced electronic radon detection systems.
How do radon monitors function, and how reliable are they?
Radon monitors detect radon levels in your home, with some using passive methods like charcoal canisters while others use active methods with continuous monitoring. These devices are highly reliable when used as directed and maintained properly.
What steps are involved in monitoring radon levels within my home?
Monitoring radon levels involves selecting an appropriate detector, placing it in the lowest lived-in level of your home, and following the testing period specified by the device before sending it to a lab for results, if necessary.
How often should I test for radon?
It’s advisable to test every two years or after any significant home renovation that could alter radon levels.
Can radon levels fluctuate over time?
Yes, radon levels can vary due to changes in weather, home ventilation, and soil conditions. Continuous radon monitoring with a smart radon detector ensures you’re always informed.
What time of year is radon levels the highest?
The highest radon levels are typically observed during the winter months. But, depending on location and conditions, high radon levels can be detected all year.
Is radon only a concern in certain areas?
While some regions have higher radon prevalence, any home can have elevated radon levels. Testing is the only way to know for sure.







