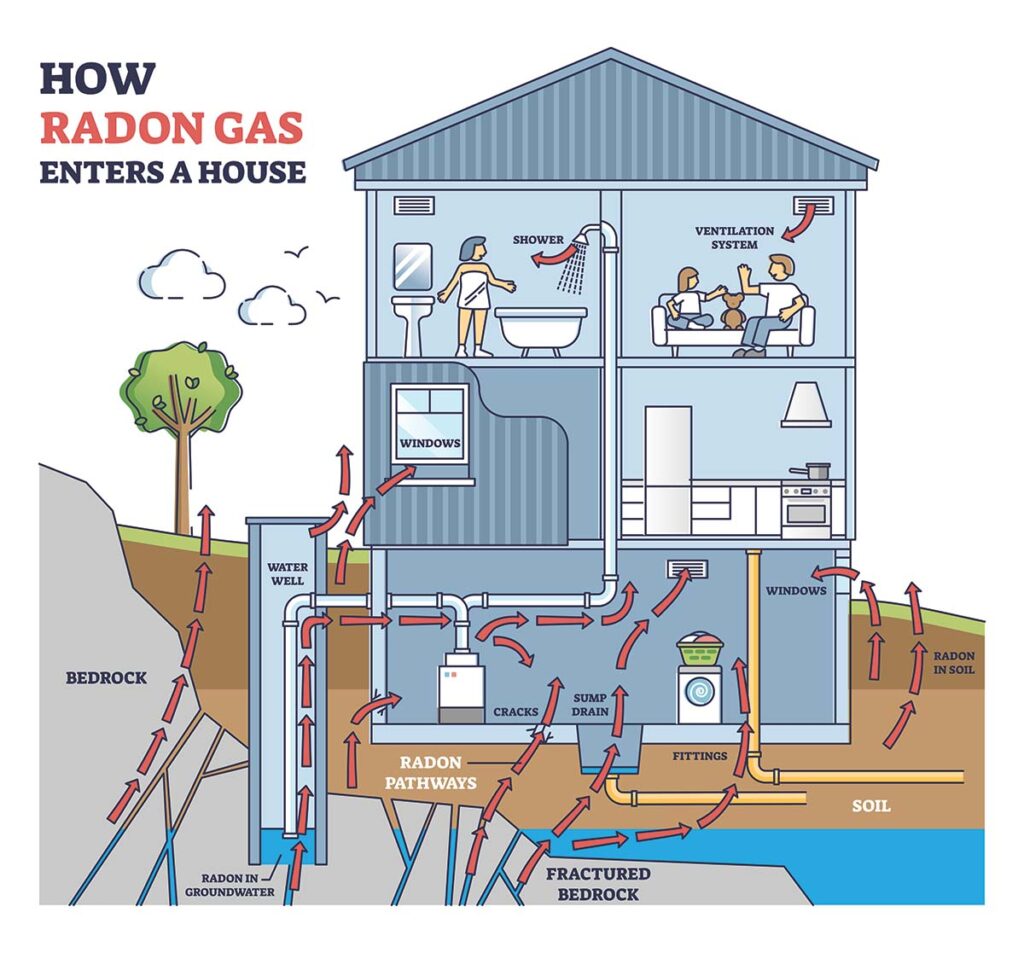
Radon is a naturally occurring radioactive element found in soil and rock. It’s a colorless, odorless gas that permeates homes through cracks in foundations, walls, or flooring.
Long-term radon exposure is the second leading cause of lung cancer after smoking. Homeowners and renters should understand how to manage and reduce radon levels.
Reducing radon levels in your home involves steps;
- Conduct a radon gas test for your home (DIY or professionally).
- Consult a professional to accurately assess high radon levels in your home and determine the best mitigation measures.
- Seal cracks and openings in the foundation to prevent radon from entering your home.
- Install a radon mitigation system to reduce radon levels permanently.
- Consider using a radon detector to monitor radon levels over time.
- Regularly test your radon mitigation system to ensure its effectiveness.
Radon testing is the only way to determine the presence of dangerous radon gas. The EPA recommends mitigating radon levels above 4.0 picocuries per liter (pCi/L).
Mitigation can include simple DIY techniques like sealing the floor and wall cracks and installing a professional radon mitigation system.

Exploring Radon and Its Hidden Dangers
Before diving into methods to reduce radon levels, it’s crucial to understand what radon is and its associated health implications. This knowledge forms the basis for recognizing the importance of mitigating radon exposure.
What Exactly is Radon?
Radon is a radioactive gas that occurs naturally as a byproduct of the decay of uranium found in soil and rocks. You cannot see, smell, or taste radon, which makes it easy to ignore, but its presence in homes and buildings can pose significant health risks.
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) categorizes radon as a carcinogen and recommends all homeowners test their homes for dangerous radon levels.
The Health Risks Linked to Radon Exposure
Radon exposure is a serious health concern, second only to cigarette smoke for causing lung cancer. The EPA estimates thousands of lung cancer deaths each year are attributable to radon exposure.
The risk increases if you smoke and are exposed to high levels of radon. Long-term radon exposure can lead to lung damage and significant health issues, emphasizing the importance of regular home testing and mitigating elevated radon levels.
How to Conduct Radon Testing in Your Home
Before considering radon mitigation, it’s crucial to test your home to determine the presence and level of radon. Accurate testing is the only way to know whether you and your family are at risk from radon.
Timing and Methods for Radon Testing
Best Times to Test: Aim to test for radon during stable weather conditions, like in the calm of spring or winter when your home is sealed tight. This gives the most reliable results.
It’s a good idea to test every two years or after making significant changes to your home, as these can alter radon levels.
How to Conduct the Test: You can easily get a radon test kit in short-term or long-term versions, depending on how quickly you need results or how detailed you want the analysis.
The testing process usually involves placing the kit in the lowest part of your home where you spend time. After testing, the kit is sent to a lab for radon level analysis, typically reported in picocuries per liter (pCi/L).
Understanding Your Radon Test Results
What’s Considered Safe: Technically, no radon level is completely safe, but the EPA suggests taking action if your home’s levels are at or above 4 pCi/L.
When to Mitigate: If your test shows radon levels of 4 pCi/L or higher, it’s time to look into radon reduction systems to bring those levels down.
Expect Some Variability: Radon levels can fluctuate, so different kits or tests might show varying results at other times. For a more accurate picture, consider multiple or long-term tests.
Effective Ways to Lower Radon Levels in Your Home
Addressing high radon levels in your home is crucial for ensuring a healthy living environment. You can employ immediate and long-term strategies to manage and reduce radon levels effectively.
Immediate Actions for Radon Reduction
If you find elevated radon levels in your home, here are some quick steps to take:
- Seal Cracks and Openings: Start by sealing cracks in your floors and walls with caulk. This helps prevent radon from entering your home.
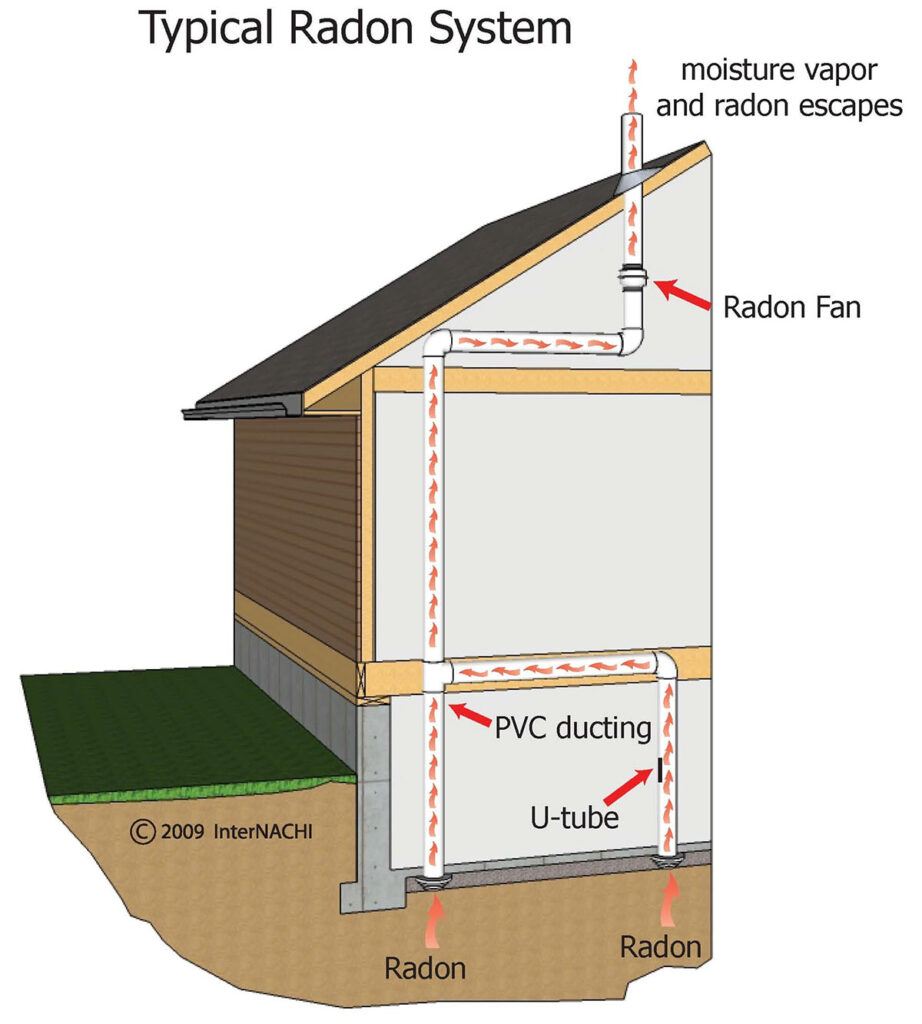
- Enhance Ventilation: Implement sub-slab depressurization. This involves installing a ventilation system that draws radon from beneath your home and expels it outside, reducing indoor radon levels.
Long-Term Strategies for Radon Management
For sustained radon control, consider these long-term solutions:
- Regular Radon Testing: Keep testing your home for radon periodically. This is crucial to ensure radon reduction measures are effective and radon levels remain low over time.
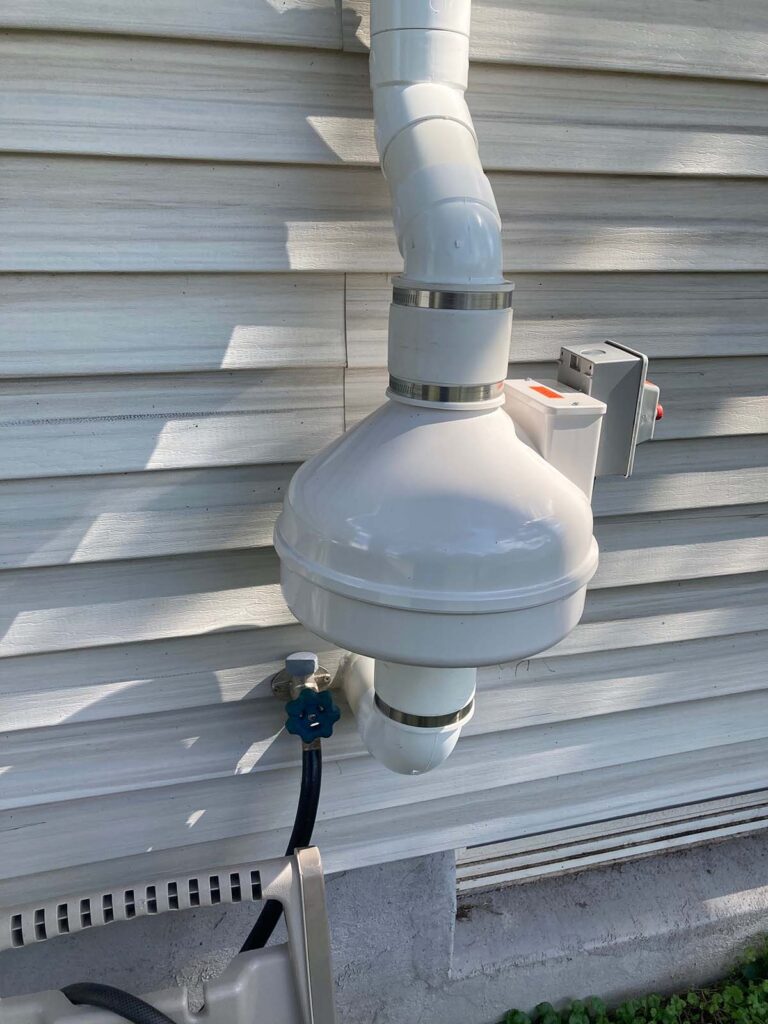
- Install a Radon Mitigation System: A more comprehensive approach is to install a radon mitigation system. This typically includes a vent pipe system and a fan, continuously redirecting radon gas from your home to the outside.
Professional Radon Mitigation for a Safer Home
When it comes to radon, ensuring your safety is crucial. To effectively reduce radon levels, it’s often necessary to rely on the expertise of a professional radon mitigation contractor.
Selecting a Radon Mitigation Contractor
Here’s how to find a qualified radon mitigation contractor:
- Look for Certification: A certified radon mitigation contractor is trained and adheres to recognized radon reduction standards. Check for certifications from organizations like the National Radon Proficiency Program (NRPP) or the National Radon Safety Board (NRSB).
- Do Your Research: Seek contractors with a track record of experience and positive client feedback.
- Compare Estimates: Get quotes from multiple contractors to evaluate their assessment and mitigation recommendations.
Understanding Radon Mitigation Systems
Professional radon mitigation systems are designed to lower radon levels in your home. Familiarize yourself with these common systems:
- Active Soil Depressurization (ASD): This popular and effective system uses a vent pipe and fan to draw radon from beneath your house and release it outside. Some ASD systems can reduce radon levels by up to 99%.
- Sealing: Radon reduction involves sealing cracks and openings in your home’s foundation to prevent radon entry.
Additional Considerations in Radon Mitigation
- Air Conditioning’s Role: While air conditioning can impact indoor radon levels, it’s not a reliable mitigation method. It may help circulate and dilute radon but doesn’t remove it.
- Basement Remediation: In basements, sub-slab depressurization systems are often recommended. Sealing floors and walls can help but should be part of a broader mitigation strategy.
- Post-Mitigation Timeframe: Radon levels typically decrease within 24 hours of mitigation, with stabilization occurring over a few days. Regular testing is crucial to ensure ongoing safety.
DIY Radon Reduction Strategies
While professional mitigation is often necessary, these DIY techniques can help lower radon levels:
- Sealing and Caulking: Use polyurethane caulk or hydraulic cement to seal cracks in basement floors and walls, focusing on areas around utility pipes.
- Improving Natural Ventilation: Open windows strategically to enhance air circulation, especially in lower levels.
- Installing Ventilation Fans: Place fans in basements or crawl spaces to expel air outside, creating a pressure difference that helps keep radon out.

Legal and State-Specific Radon Information
In the United States, radon exposure mitigation and awareness are governed by state-specific laws and EPA guidelines. These regulations are vital for ensuring the safety of your indoor environment.
State Radon Laws and Regulations
Each state has its own set of laws and regulations about radon gas. For example, some states mandate radon disclosure during real estate transactions, requiring a warning statement about radon or other radon information provided.
Other states may have specific requirements for school radon testing, aiming to reduce exposure in educational environments. Reviewing the radon laws specific to your state is important to understand the guidelines that apply to you.
Information about these regulations can sometimes be found on state health department websites or through initiatives promoting radon risk reduction.
Finding Your State Radon Office
Your State Radon Office is a key resource for information and assistance with radon-related concerns. It can guide you on how to test for radon, interpret your test results, and find qualified radon mitigation professionals if necessary.
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) provides a list of state-specific radon contacts and resources that can be instrumental in helping you manage radon risks. Many state radon offices also collaborate with the EPA to develop and implement radon control programs designed to protect public health.
Financial Factors of Radon Mitigation
When considering radon mitigation for your home, it’s important to understand the costs can vary, and financial assistance options may help with the investment.
Estimating Radon Mitigation Costs
To accurately estimate the radon mitigation costs, you must first conduct a radon test to understand the level of mitigation needed.
Professional radon mitigation can range from $800 to $2,500, depending on the complexity of your system and the radon levels in your home.
Factors influencing the cost include the size of your home, the type of foundation, and the radon reduction method chosen. For a tailored estimate, consult with a certified radon mitigation professional.
- Diagnostic Evaluation: $150 to $250
- Radon Mitigation System Installation: $800 to $2,500+
- Post-Mitigation Testing: $50 to $150
Financing Radon Reduction Measures
Financing the costs of radon mitigation doesn’t have to be a barrier. Explore different financial assistance programs available through state grants or local initiatives.
Some states provide low-cost loans, tax incentives, or rebate programs to cover the expenses of reducing radon levels in homes. Additionally, non-profit organizations often offer financial help to those unable to afford mitigation costs.
Always verify the credentials of any financial assistance program to ensure it’s reputable and you’re eligible.
- Explore State Grants & Assistance Programs
- Investigate Local Rebates & Incentive Offers
- Review Non-Profit Aid Options
FAQs
Is there a difference in radon levels across various home styles?
Different home designs, like ranch vs. multi-story, can impact how radon accumulates and disperses within the structure. Homes with basements are most susceptible.
How does the age of a home affect its susceptibility to radon?
Older homes are naturally well-ventilated. They have more cracks and openings, potentially increasing radon entry. Newer homes can also be at high risk due to air-tight sealing, which can trap and allow radon gas to accumulate.
Do weather conditions influence the effectiveness of radon mitigation systems?
Certain weather conditions, like heavy rain or snow, can affect the pressure differentials and the efficiency of radon mitigation systems.
Can regular home maintenance impact radon levels?
Consistent home maintenance, like sealing basement and foundation cracks and ensuring proper ventilation, can help maintain lower radon levels.
Does the use of air purifiers or dehumidifiers affect indoor radon levels?
Air purifiers and dehumidifiers can alter indoor air quality but are ineffective in reducing radon levels. Read more oncan air purifiers remove radon gas.
Does the presence of a basement or crawl space significantly increase radon risk?
Basements and crawl spaces can be more prone to radon entry due to their proximity to the ground.







