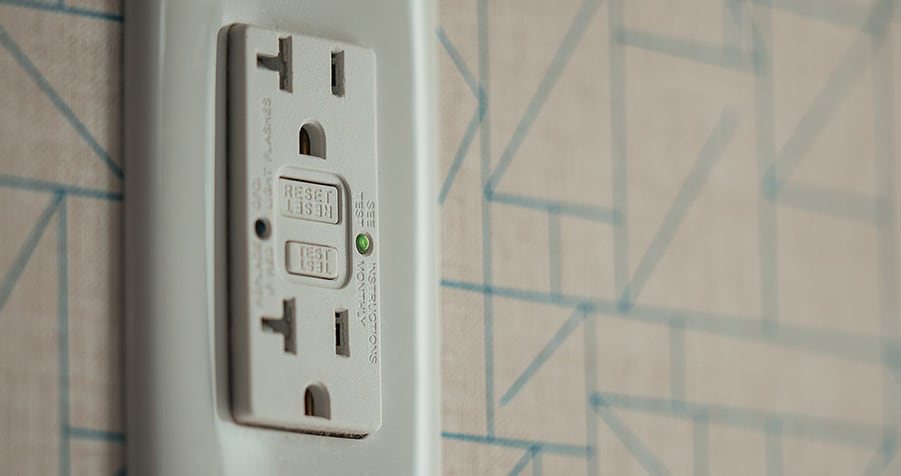
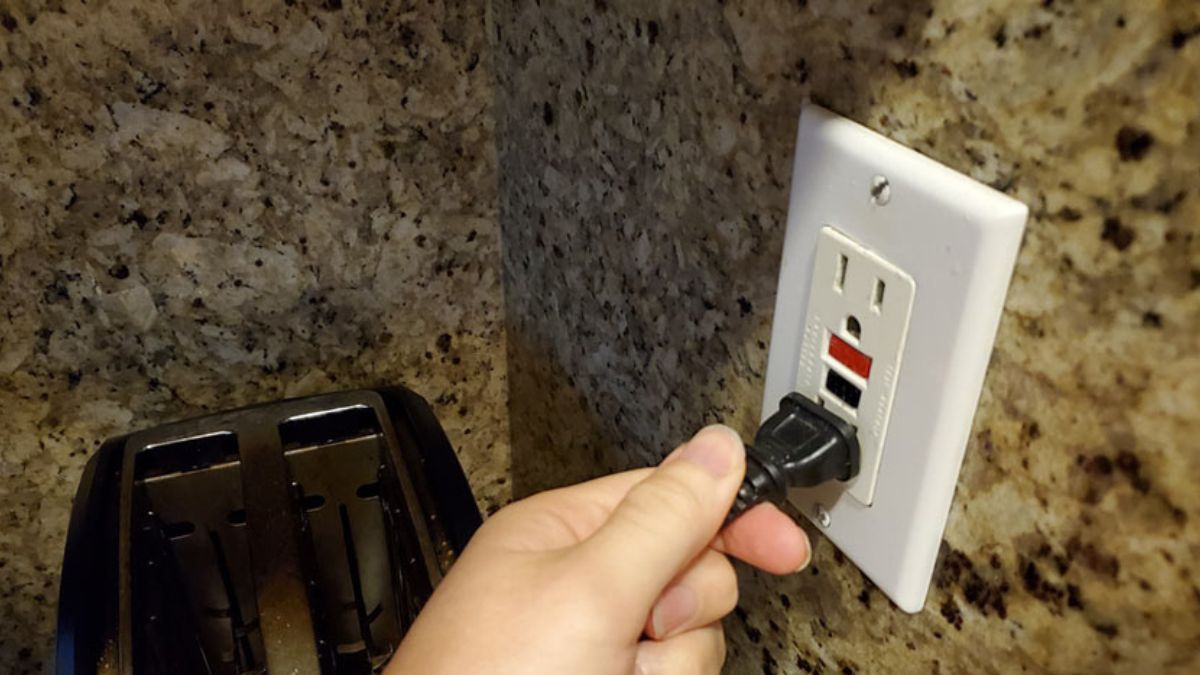
It can be frustrating if your ground fault circuit interrupter outlet (GFCI) is not working or keeps tripping. But don’t worry, we’re here to help! In this troubleshooting guide, we’ll walk you through fixing a GFCI outlet that’s not working or resetting.
GFCI outlets have been around since 1971. However, over the years has steadily been incorporated into more areas of our homes. These devices don’t last forever and eventually wear out, causing them not to work or reset.
A GFCI outlet that is not working or won’t reset is often caused by moisture, a tripped breaker, age, or faulty installation. A GFCI outlet will last about 10 and 25 years in most cases. However, certain conditions may cause GFCI electrical outlets to fail or trip frequently.
A GFCI outlet not working is considered a dead outlet. A dead outlet is an electrical receptacle that does not have an electrical current to it. When a GFCI trips, the electrical current to the outlet plug slots is disrupted.
Get FREE estimates from licensed electricians in your area today. Whether you need to replace an outlet, hang a ceiling fan, a new electrical panel, or repair wiring, We Can Help!
As stated above, there are three main reasons for a GFCI to not work correctly or to trip frequently.
- GFCI outlets are supposed to trip when the sensor detects an imbalance across the hot and neutral terminals causing a ground fault. If the GFCI detects moisture it trips to prevent electric shock.
- A tripped breaker inside the main electrical panel will cause no flow of electricity to the GFCI outlet. If the outlet’s breaker trips it may indicate an electrical problem inside the circuit breaker box or your home’s electrical system.
- GFCI outlets have a sensor that monitors electrical current and trips to prevent electrical shock. However, as the GFCI ages, the sensor will eventually fail and not reset requiring replacement.
- Faulty installation or loose wires can cause a GFCI to trip. Loose connections will create imbalances tripping the GFCI and cutting the power supply to the outlet.
Since there are multiple reasons why a GFCI trips or is not working, troubleshooting is best done by a professional electrician.
The GFCI is Detecting Moisture
GFCI receptacles are used in such environments (in kitchens, and outside areas, for example) that can easily lead to the receptacles being subject to more than the normal moisture levels.
Moisture is hazardous and can cause different electrical ground faults that will cause the outlet to trip to prevent any electrical hazards.
If a ground fault occurs somewhere along the electrical circuit, the GFCI will immediately detect it and trip.
GFCI Life Expectancy
The lifespan of an outlet is not an exact science. Like anything else we purchase, you get what you pay for. Cheaper unbranded GFCIs often break down quickly. GFCIs located outdoors won’t last as long as GFCIs located indoors.
GFCI outlets can last a long time. They should last anywhere from 10 to 25 years before needing replacement. However, as we will find out, this time can vary greatly depending on many different factors.
In some cases, a GFCI receptacle can go bad in as little as 5 years.
The environmental conditions, any electrical surges and faults, any natural wear and tear, and more can influence and cause a GFCI outlet to go bad sooner than expected.
A malfunctioning GFCI outlet may constantly trip or even trip in an open position where the electrical current flows.
What Causes a GFCI Outlet to Go Bad?
Two main things may cause a bad GFCI outlet.
Considering these will allow you to have the right expectations about how long your GFCI outlet may last.
1. Where the GFCI is Located
GFCI outlets are a staple in modern-day homes. The National Electrical Code (NEC) requires GFCI outlets near a water source such as kitchens, bathrooms, laundry rooms, garages, and exteriors. They are considered one of the must-have safety devices in any home.
At one time, GFCI outlets were only required around sinks in bathrooms and then later in kitchens. NEC did not require washing machines to have GFCI outlets; now they do.
GFCI technology has continued to advance over the years. Bad GFCI outlets are common in home inspection reports because most people fail to test them routinely.
National residential electric codes now require GFCI protection on 120-volt 15 to 20 amps single phase outlets in all wet areas. These are a few of the required areas:
- Kitchens
- Laundry and other utility rooms
- Bathrooms
- Garages
- Outdoor locations
- Unfinished basements and crawl spaces
- Pools and spas
GFCI outlets protect areas and rooms with a high risk of a ground fault.
Many of these can place the GFCI outlet in an environment which can expose it to a lot of water, humidity, moisture, high or low temperatures, excessive sunlight exposure, the elements, and more.
Each of these is very likely to affect the natural wear and tear of the outlet in different amounts, causing the GFCI outlets not to last as long as initially expected and break down sooner.
2. Usage
The other significant determining factor in how long a GFCI receptacle will last is the problems it has encountered and used, including:
- Overloaded electrical circuits
- Electrical faults
- Electrical surges
- Faulty wiring
- Reinstallation of the receptacle in different places
All of these and their frequency will speed up the wearing out of the outlet. And as a result, a GFCI can go bad sooner than expected.
If we plug in one too many electrical appliances into one circuit, we can easily overload it and cause the GFCI breaker to trip. The GFCI receptacle does that to prevent any damage from overheating.
Also, faulty or malfunctioning electrical tools, appliances, and devices can cause an electrical overload. Some electrical appliances like freezers and refrigerators can cause GFCI outlets to trip frequently.
How to Find out if the GFCI Outlet Has Gone Bad
We recommend you regularly test the GFCI outlets you have installed in your home. Manufacturers suggest you test GFCI outlets once every month.
When considering the safety of a building or a home, GFCI outlets are a must-have, which is why the NEC continues to expand the use of GFCIs.
Although GFCIs may work for many years, they may also fail without any warning. Older GFCIs can even fail and not trip in the presence of electrical faults or overcurrents.
Following the troubleshooting recommendations, we can ensure they are working as intended.
How to Troubleshoot a GFCI Outlet
To troubleshoot your outlet, you need to:
- First, unplug any electrical devices that are plugged into the circuit you will be testing. Especially if you have plugged in more delicate equipment like computers, smartphones, and laptops.
- Press the Test button on the outlet. This will cause it to trip and cut out the power to the outlet.
- Using something small like a night lamp, test if there is any electricity running by plugging it into the outlet. It should not turn on. After that, unplug the lamp.
- Now press the Reset button. This will restore the power to the circuit. Using the lamp method again, plug it in. The lamp should turn on.
If the GFCI fails this test, a new outlet may be needed. However, other electrical issues may exist and you should call a licensed electrician for further troubleshooting.
Troubleshooting a Self-Testing GFCI
The newer models of GFCI receptacles (usually the ones produced after 2015) will most likely be self-testing.
They come with a light indicator that shows if the outlet is working correctly.
- If a green indicator light is on, the outlet is working as intended.
- if the outlet has a flashing (or solid) red light, this means that it has been compromised in a certain way.
They will still have the usually Reset and Test buttons on them, so you can also manually test the outlet.
Loose Electrical Connections Causing a Short Circuit
Anyone who has dealt with a tripping GFCI knows how annoying it can be. I want to stress the importance of never ignoring a GFCI outlet that constantly trips.
Loose wiring can also cause the receptacles to trip more frequently than necessary. Often there will be loose electrical connections located on the branch circuit that create a short circuit and cause a tripped circuit breaker or GFCI. The GFCI or breaker may reset only to trip again.
The loose wire connector could be anywhere on the branch circuit. Electrical work like this should be done by a qualified electrician.
How to Extend the Life of a GFCI Outlet
You can make these steps to extend the life of your GFCI as long as possible.
- Don’t unplug electrical devices by pulling on the cord as this can detach the outlet from the wall.
- Create a habit of switching off devices that you are not using.
- Do not overload the GFCI receptacle by plugging in high-demanding electrical appliances or using power strips.
- Have the wiring inspected in order to confirm it is up to code, and no bad wiring practices have been used.
- Avoid exposing the receptacle to water, chemicals, UV light, etc.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can a GFCI Outlet Fail?
Yes, a GFCI outlet can fail. You can expect a GFCI outlet to work correctly for 10 to 15 years before starting to wear out significantly and going bad or failing.
See our article Bad GFCI Receptacle – Can a GFCI Outlet Fail?
How Do GFCI Outlets Work?
A GFCI (or Ground-fault circuit interrupter) equipped outlet is a safety device that protects against electrical shocks. The GFCI will automatically cut off power when it detects a problem in the electrical current.
See our article How GFCI Outlets Work and Why We Need Them.
Are GFI and GFCI the Same?
The terms GFI and GFCI are often interchanged. Ground fault interrupter (GFI) and ground fault circuit interrupter (GFCI) both protect a branch circuit against ground faults. Some manufacturers use GFCI while others use GFI.
Get FREE estimates from licensed electricians in your area today. Whether you need to replace an outlet, hang a ceiling fan, a new electrical panel, or repair wiring, We Can Help!
See our article GFI vs GFCI: Are They the Same?
Also, consider these electrical articles: