Cinder block foundation problems can turn a dream home into a homeowner’s nightmare. These issues, often hidden beneath the surface, can cause significant damage and lead to costly repairs if not addressed promptly.
Unlike poured concrete slab foundations, cinder block foundations are made with hollow (or partially hollow) blocks stacked and held in place with mortar. Cinder block foundation walls can be built above or below ground, depending on the application and desired results.
Various elements can contribute to issues with cinder block foundations, such as faulty construction, excessive dampness, insufficient insulation, and seasonal fluctuations in temperature and humidity. Here are some typical indicators of complications with cinder block foundations:
- Cracks: The presence of foundation wall cracks in the walls of a cinder block foundation can signal potential foundation failure. Horizontal cracks and stair-step cracks are especially worrisome and require immediate attention.
- Inconsistencies: A foundation that isn’t even can lead to complications with the building’s walls and roof. A non-level foundation can result in uneven walls and challenges during roof installation.
- Malfunctioning Doors: Foundation settling can lead to misaligned doors, making them hard to open or close correctly.
Get FREE quotes from local foundation repair contractors in your area today. Whether you need a pier replaced, basement waterproofing, or a full foundation replacement - We Can Help! All Contractors are screened, licensed, and insured.
Addressing structural failure with cinder block foundations promptly is crucial to prevent further harm to the structure. If you observe any signs of foundation problems, it’s advisable to seek professional advice to determine the most effective solution.
The concrete block foundation’s life expectancy is 50-100 years, depending on the build quality and local climate. Cinder block foundation deterioration may occur as it ages, leading to cracking or crumbling. Avoid wet conditions and keep vegetation away from the foundation walls to prevent this.
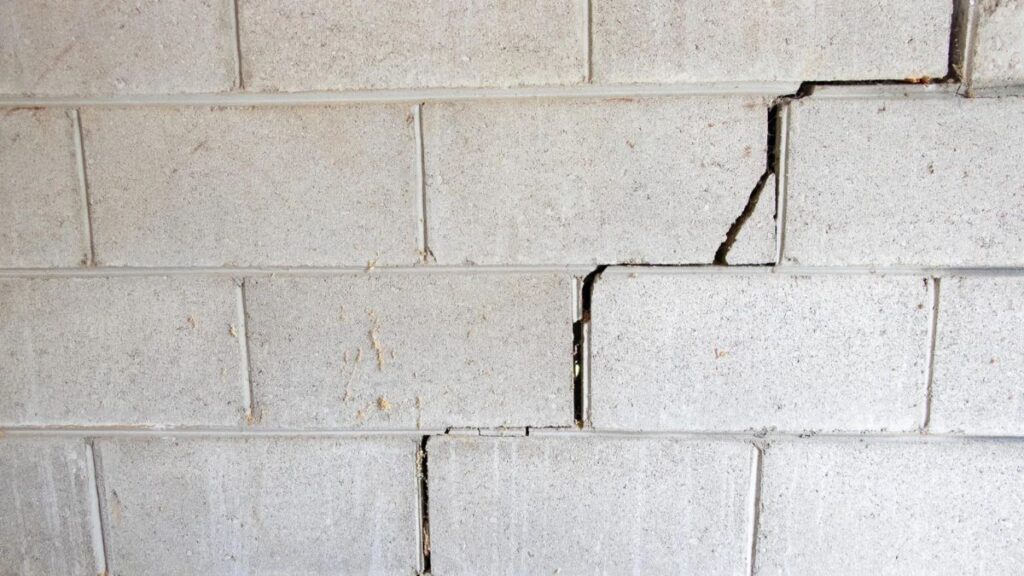

Common Problems with Cinder Block Foundations
Like brick foundations, Cinder block foundation problems arise from environmental factors like soil movement caused by seasonal fluctuations in temperature or water damage due to poor drainage systems on-site.
- Cracks in the cinder block foundation can signify structural damage, especially if they widen or grow over time. Cracks can occur in the mortar joints or the concrete blocks themselves.
- Cinder block walls are more likely to suffer from bowing and buckling due to the number of joints between blocks that can shift. This can be a result of poor construction or underground lateral water pressure.
- Bulging concrete block walls with horizontal cracking are at risk of sudden catastrophic collapse, potentially causing injury and property damage.
While cinder block foundations are sturdy and long-lasting when correctly built and maintained, they can still experience specific problems over time.
Cinder block foundations often encounter common issues such as horizontal cracks, also known as step cracks, in walls or floors resulting from uneven weight distribution.
They can also experience sagging ceilings due to settling foundations, doors, or windows that no longer fit properly due to shifting structures beneath them. Additionally, water seepage can occur as a result of inadequate waterproofing.
If you start noticing any of these problems in your home, taking action quickly is essential to avoid further damage.
Soil Movement and Settlement: The Silent Culprit
Soil movements are among the most common culprits of cinder block foundation problems. This type of foundation is typically built on poorly prepared soil, which can lead to issues down the line.
Most problems associated with concrete-block foundations can be traced to improper drainage, leading to excessive moisture levels around the foundation.
The ground beneath a building can shift due to several factors, including changes in temperature, heavy rainfall, and natural disasters like earthquakes.
Expansive soil is a type of soil that can expand and contract due to changes in moisture or humidity. It can cause problems with foundations, walls, and other structures because the expansion and contracting can cause significant damage.
Expansive soils are found mainly in areas where clay is present in the soil, such as in the Southern United States and California.
A contraction of soils during drought seasons creates voids under footings and foundations. Voiding occurs when water erodes or is removed from the soil surrounding a foundation.
When the soil beneath a building shifts or settles unevenly, it can cause cracks in the foundation walls or floors, including concrete foundation walls.
Over time, these cracks can grow larger and significantly weaken the structure. The issue starts small but can quickly escalate to something more serious if left unaddressed.
To prevent this problem from occurring or worsening, proper site preparation should be done before construction starts.
This step involves site inspection and leveling out any uneven areas to ensure the foundation is built on stable ground.
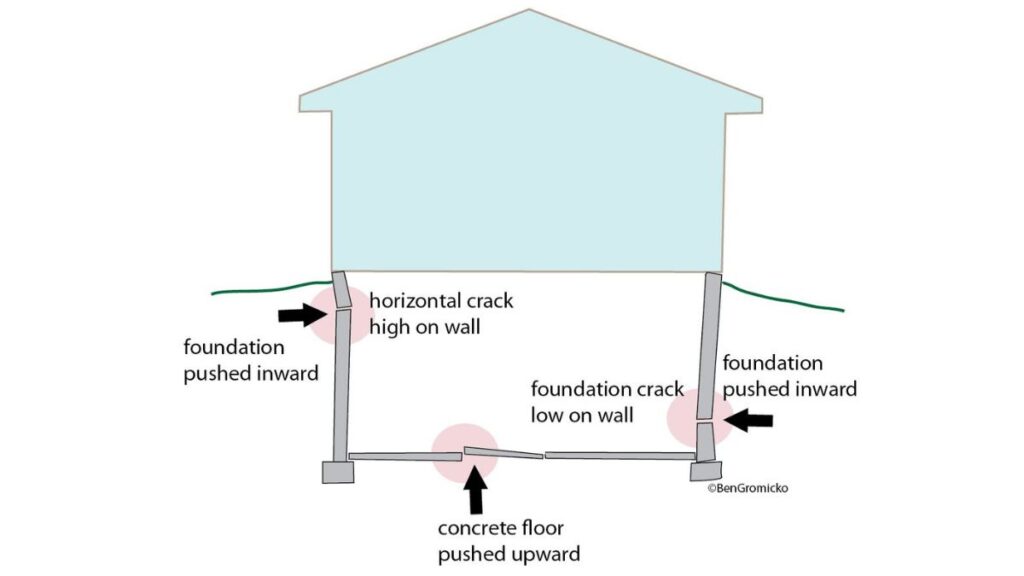
Water Damage and Drainage Issues: Enemy Number One
Water damage is another significant cause of cinder block foundation problems. When water accumulates around a building’s foundation due to poor drainage or inadequate waterproofing measures, it can lead to severe damage over time.
Waterlogged soil exerts extra on foundations which facilitates cracking.
- Seasonal expansion and contraction of the soil around the foundation can lead to issues like cracking and bowing.
- Hydrostatic Pressure is a significant difficulty for basement walls. Because block foundations are surrounded by soil, whatever affects the soil (like water content) can impact the foundation.
Hydrostatic pressure is the force of water pressing against a basement wall or foundation caused by standing water around or beneath it. This can cause cracks in the foundation and damage to walls, floors, and ceilings. Signs include wet spots on interior walls, water seeping through basement windows, and buckling floors.
A wet basement for extended periods can lead to mold growth, a huge health concern. It can also cause structural damage to the walls and floors in the basement and lower levels of your home.
In addition to weakening cinder block foundations over time, water damage also increases the risk of mold growth within your home’s walls and floors, leading to health problems for you and your loved ones.
To remedy this challenge effectively, proper gutter systems with drains leading away from the house should be installed immediately after construction finishes while ensuring proper waterproofing measures are implemented during construction.
Poor Construction Practices: The Human Factor
Poor construction practices during initial installation sometimes contribute to weak cinder block foundations.
- Poor construction practices can lead to various foundation problems. This includes improper installation and the use of inadequate materials.
- Lack of proper insulation can lead to issues like moisture intrusion, damaging the foundation over time.
Common mistakes include inadequate materials usage (both in incorrect quantity and inferior quality), improper reinforcement, and lack of proper drainage.
It is important not to cut corners or use sub-par materials during construction. Working with experienced foundation specialists who understand the nuances of building cinder block foundations is essential to avoid this issue.
When selecting a contractor, be sure to check their references and verify that they have experience working with cinder block foundations specifically.
It is important to take all necessary precautions during construction to prevent foundation problems caused by soil movements, water damage, drainage issues, and poor construction practices.
Signs of Cinder Block Foundation Problems
Cinder block foundation problems can manifest themselves in several ways. Watch out for these tell-tale signs of foundation problems:
- Visible cracks, bulges, or damage to the cinder block foundation are clear signs of problems.
- Leaking or weeping tiles (drainage pipes) around your foundation are leaking could indicate a problem with the foundation itself.
- Tipping or leaning walls could be a sign of foundation issues.
Cracks in the Walls or Floors
One of the most common signs that a cinder block or concrete foundation is experiencing problems is the appearance of cracks in the walls or floors, including various types of cracks.
These cracks can range from small, such as hairline fractures, to larger and more pronounced ones, affecting the integrity of the cinder block and concrete foundation walls.
These cracks can range from small, such as hairline cracks, to larger and more pronounced ones.
Cracks in cinder block walls and concrete block walls can occur for various reasons, including soil movement and settlement, water damage, poor construction practices, and more.
It is important to promptly identify and address these cracks to prevent further damage and ensure the stability of the walls.
Diagonal cracks or vertical cracks are also common and should be identified early on to prevent them from worsening. It is important to address these cracks promptly to maintain the structural integrity of the walls.
If you notice any cracks forming in your cinder block foundation wall or floor – no matter how small they may be – it’s important to have them inspected by a professional foundation contractor.
They can provide an assessment of the severity of the problem and recommend a course of action to repair any damage that has been done.
Uneven Floors or Sagging Ceilings
Another sign that your cinder block foundation indicates experiencing problems is uneven floors or sagging ceilings.
If you notice that your floors, including concrete floors, are not level – such as if they slope towards one side of the room – this could indicate that there are issues with your foundation.
Similarly, if you notice that your ceiling seems to sag in certain areas, this could also be a sign of foundation problems.
If left untreated, uneven floors and sagging ceilings can lead to serious structural issues with your home.
Not only can this make it difficult to sell your property down the line, but it can also pose safety risks for occupants.
Doors and Windows that Don’t Close Properly
A third common sign of problems with your cinder block foundation is doors and windows not closing properly. This could mean that they stick when you try to open or close them or don’t align properly when closed.
This issue occurs because the foundation has shifted or settled over time, causing the door and window frames to become misaligned. These often accompany diagonal cracks over the door or window frame.
If you’re experiencing difficulty with opening or closing your doors and windows, it’s important to have your foundation inspected by a professional.
They can provide an assessment of the severity of the problem and recommend a course of action to repair any damage that has been done.
If left untreated, this type of issue will only worsen over time, potentially leading to more significant structural issues with your home.
Solutions for Cinder Block Foundation Problems
If you’re experiencing cinder block foundation problems, you must address them early to prevent costly structural damage. There are three things you can do today, including:
- Proper drainage around the foundation can help prevent many common problems.
- Regularly inspecting the foundation for signs of damage can help catch problems early before they become more serious.
- If damage is found, it’s often best to hire a foundation specialist to repair it. DIY repairs can often make the problem worse if not done correctly.
Related Reading: Expert Guide to Foundation Crack Repair Methods
Waterproofing and Drainage Solutions: Keeping Water Out
One of the most common problems with cinder block foundations is water damage, including water leaks and basement leaks.
This can occur due to various reasons, such as poor drainage, excess moisture in the foundation’s soil, and broken pipes or plumbing leaks.
Waterproofing and drainage solutions are necessary to prevent further damage caused by water infiltration.
The first step in waterproofing your foundation, including the basement floor slab, is to seal all cracks, mortar joints, and gaps to prevent excess water from seeping into your basement floor or crawlspace.
This can be done using various sealants such as hydraulic cement or epoxy injections. However, this can’t solve all your problems if your foundation has other issues.
To address any underlying drainage issues, a French drain system can be installed around the perimeter of your home.
A French drain consists of a trench filled with gravel or rock that redirects excess moisture away from your home’s foundation and into an area where it can safely disperse without causing any damage.
Reinforcement with Steel Beams or Anchors: Adding Strength to Your Foundation
Reinforcement is necessary if you have noticed signs of settling or shifting in your cinder block foundation walls due to weak soil conditions or unstable construction practices.
Typically this involves using steel beams that are placed along the length of the basement wall either vertically between blocks or horizontally across multiple blocks.
A professional contractor will assess which type of beam would be most effective for your particular needs based on factors such as weight-bearing requirements and potential space constraints within the walls themselves.
Once installed properly, these steel beams provide additional support to help distribute weight evenly along all points of contact along each block. Another option for reinforcing cinder block foundations is through anchor installation.
This method involves regularly drilling holes through each block and then inserting steel anchor rods into the holes.
The rods are then tightened with nuts and washers to create tension, which helps stabilize the foundation walls and prevent further shifting or settling.
Repairing Cracks with Epoxy Injections: A Cost-Effective Solution
Various factors, including soil movement, water damage, and general wear and tear over time can cause foundation cracks or basement wall cracks.
If left unaddressed, these foundation cracks can lead to more serious structural damage down the line.
One cost-effective solution for repairing cracks in cinder block foundations is through epoxy injections. This involves filling in the cracks with an epoxy resin that hardens to form a strong bond within the wall.
Epoxy injections are particularly effective for smaller cracks that do not require any additional reinforcement. However, it is important to note that these foundation repairs are unsuitable for larger or more severe cracking situations.
In those instances, reinforcement solutions such as steel beams or anchors are necessary for the long-term stability of your foundation walls. The steel rods prevent further movement allowing the epoxy to seal the various kinds of cracks.
By promptly addressing any problems with your cinder block foundation, you can ensure that your home remains stable and secure for years to come.
Prevention of Cinder Block Foundation Problems
Proper site preparation is essential to ensuring a strong cinder block foundation.
A Proper Site Preparation Before Construction Begins
Working with a qualified engineer or contractor with experience with foundations, soils, and grading is important to ensure that the site is properly prepared for construction.
The soil should be tested to determine its bearing capacity and composition.
Depending on the test results, additional measures are necessary, such as compaction or adding gravel or other materials to strengthen the soil.
Also, it is important to pay attention to both natural and man-made factors that could impact the foundation.
For example, trees near the building site can cause problems if they are too close or their roots extend under the foundation.
Nearby water sources like streams or rivers can also affect the soil’s stability if they flood or create excessive moisture issues.
Regular Maintenance and Inspections to Catch Problems Early On
Just like any other part of building foundations, a cinder block foundation requires regular maintenance and inspections to catch problems early on before they become major foundation issues.
This includes performing regular checks for signs of cracks, bulges, settling, or excessive moisture intrusion.
Homeowners are advised to inspect their foundations at least once a year. This involves checking for cracks on both interior and exterior walls.
Additionally, ensuring that doors and windows function properly, without sticking or binding when opening or closing, is essential.
Professional inspections should also be conducted every 3-5 years by an experienced structural engineer who can identify any potential issues before they lead to significant structural damage.
In particular, inspections should focus on identifying signs of water intrusion which can lead to serious problems if left unaddressed.
While it seems like an extra expense up front, investing in proper site preparation and regular maintenance and inspections can save homeowners significant time and money.
By taking these preventative measures, you can ensure that your cinder block foundation stays strong and stable for years to come.
Cinder Block Foundation Problems FAQs
We answer some commonly asked questions about cinder block foundation problems below.
Are cinder block foundations bad?
Cinder block foundations are not inherently bad but can be prone to certain issues. Cinder block foundations can face issues like cracking and shifting, but with correct construction, upkeep, and regular checks, these problems can be managed. Consulting a foundation repair contractor and addressing concerns promptly ensures the home’s durability and stability.
How long do cinder block foundations last?
Cinder block foundations’ lifespan, influenced by construction quality, maintenance, soil, and climate, can span 50 to 100 years or more. Regular checks, timely fixes, and waterproofing are key to extending their durability.
How do you know if a cinder block foundation is bad?
Visible, growing cracks in walls or floors, uneven surfaces, sagging or bowing walls, and issues with doors or windows opening or closing may all suggest potential foundation problems.
Why don’t we build houses out of cinder blocks?
Cinder blocks, while strong and moisture-resistant, aren’t typically used for entire houses due to their industrial look, poor insulation, and difficulty in modification. The labor cost and potential for structural issues like cracking and shifting make other materials more favorable for residential construction.
When to be concerned about cracks in block walls?
Concerns about cracks in block walls arise when they’re wider than 1/8 inch, near corners or openings, horizontal or diagonal, or growing over time. It’s advisable to consult a professional for any noticeable cracks.
Conclusion
The foundation is vital to your home’s stability, with cinder block foundations being common but susceptible to issues like cracks and moisture damage.
Regular maintenance, early problem detection, and prompt repairs are crucial to prevent extensive and costly damage. If issues are suspected, professional inspection and intervention are recommended to maintain the home’s structural integrity.








